The Versatility and Benefits of Gabions
Gabions, originating from the Italian word gabbione, meaning “big cage,” are wire mesh cages or boxes filled with rocks, concrete, or other materials. They have been utilized for centuries in various engineering and architectural applications, primarily due to their strength, durability, and environmental advantages. This article explores the versatility, benefits, and applications of gabions in today's world.
Historical Context and Evolution
Historically, gabions were used primarily in military fortifications. Soldiers would fill these wire mesh structures with stones and place them as barriers to protect against enemy attacks. Over time, their use has expanded significantly, moving from military applications to civil engineering, landscaping, and environmental management.
Structural Integrity and Durability
One of the main reasons for the popularity of gabions in construction is their exceptional structural integrity. When filled with heavy materials, these cages can effectively withstand the forces of nature, including erosion from water flow, high winds, and seismic activity. The flexibility of gabions allows them to shift and settle without cracking, making them an ideal choice for unstable terrains.
Moreover, gabions are highly durable, often lasting for decades with little to no maintenance. The materials used for the wire mesh are typically galvanized or coated with protective substances to prevent rust and degradation, further extending the lifespan of the structures.
Environmental Benefits
Gabions are also celebrated for their environmental advantages. The use of natural materials in their construction promotes sustainability. The rocks or stones used in gabions can often be found locally, minimizing transportation energy and costs. Furthermore, gabions can facilitate natural water drainage, reducing the risk of flooding and erosion in nearby areas.
gabion1
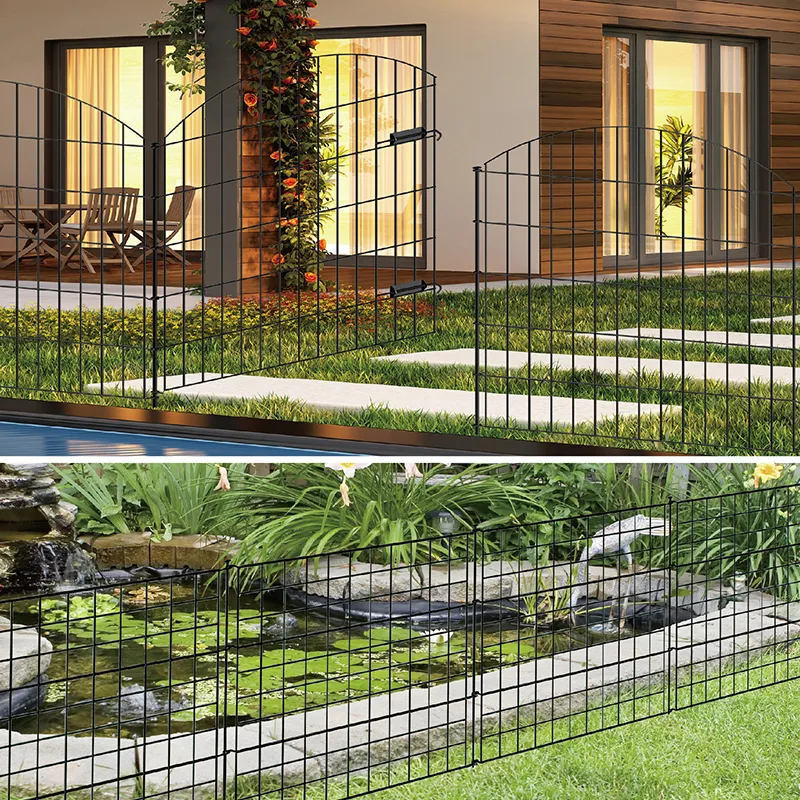

In addition, the spaces between the rocks in a gabion allow for vegetation to grow, which contributes to local biodiversity. Plant roots can help stabilize the structure and provide habitats for small animals. This symbiosis between human construction and nature showcases how gabion structures can bolster both human infrastructure and the environment.
Applications in Civil Engineering
Gabions have found a wide range of applications in civil engineering projects. They are commonly used for spillways, retaining walls, and riverbank stabilization. By constructing gabion walls along riverbanks, engineers can prevent soil erosion while creating natural habitats for wildlife.
Gabions can also be employed in landscaping designs. Gardeners and landscape architects often use them as decorative elements, creating unique features in parks and public spaces. For instance, planted gabions can serve as raised garden beds, allowing for creative and eco-friendly gardening solutions.
Economic Viability
From an economic standpoint, gabions can be a cost-effective solution for many projects. Unlike traditional solid structures, gabions require less material and labor to construct, which can drastically reduce project costs. Their longevity and low maintenance needs further contribute to their economic appeal.
Conclusion
In conclusion, gabions are versatile, durable, and environmentally friendly structures that have evolved from ancient military applications to modern-day civil engineering and landscaping solutions. Their ability to blend seamlessly into the environment while providing strength and stability makes them an invaluable tool for engineers and architects alike. As the world continues to seek sustainable and cost-effective construction methods, gabions will undoubtedly play an essential role in building resilient infrastructures that coexist harmoniously with nature.