Understanding Field Fences Protection and Boundaries in Agriculture
Field fences play a crucial role in agricultural practices and land management. They serve more than just a practical purpose; they are symbols of boundaries, security, and the management of agricultural resources. In this article, we will explore the types, functions, and significance of field fences in modern agriculture.
Types of Field Fences
Field fences come in various types, each designed to serve specific purposes. The most common types include barbed wire fences, woven wire fences, electric fences, and vinyl fences.
1. Barbed Wire Fences Typically made of twisted wire with sharp barbs, these fences are cost-effective and widely used for enclosing livestock. They are effective in preventing animals from straying and deterring intruders.
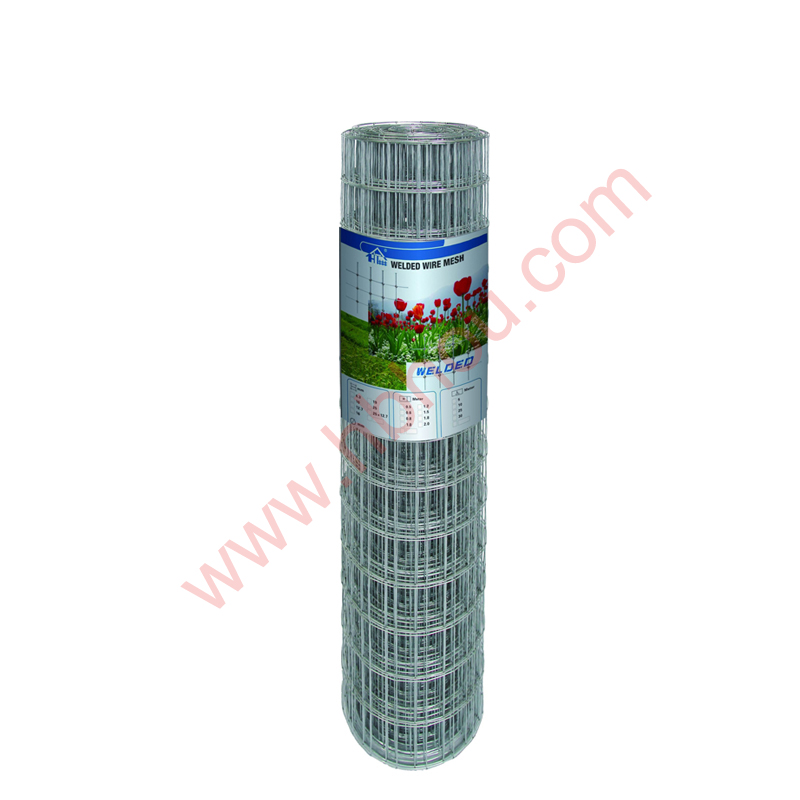
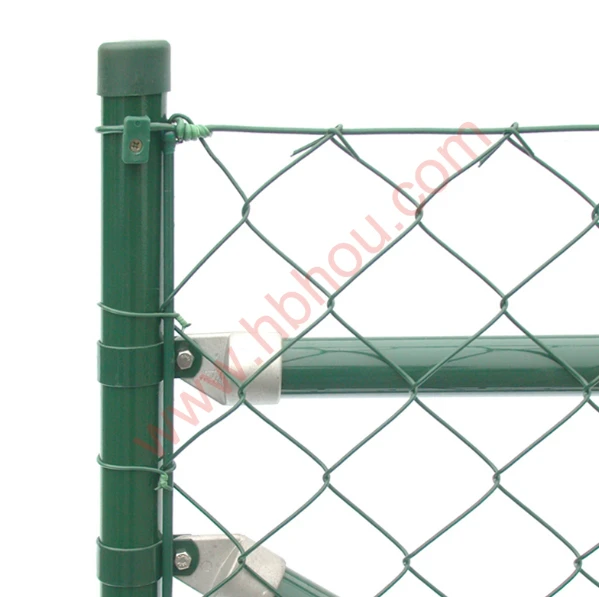
2. Woven Wire Fences This type features vertical and horizontal wires woven together to create a strong mesh. Often used for containing livestock, woven wire fences are particularly effective for keeping smaller animals in while preventing larger ones from breaking through.
3. Electric Fences These fences utilize electric current to deter animals. They are adjustable and can be particularly useful when farms need to rotate grazing areas. Electric fences are effective in containing both large and small livestock, making them a popular choice among farmers.
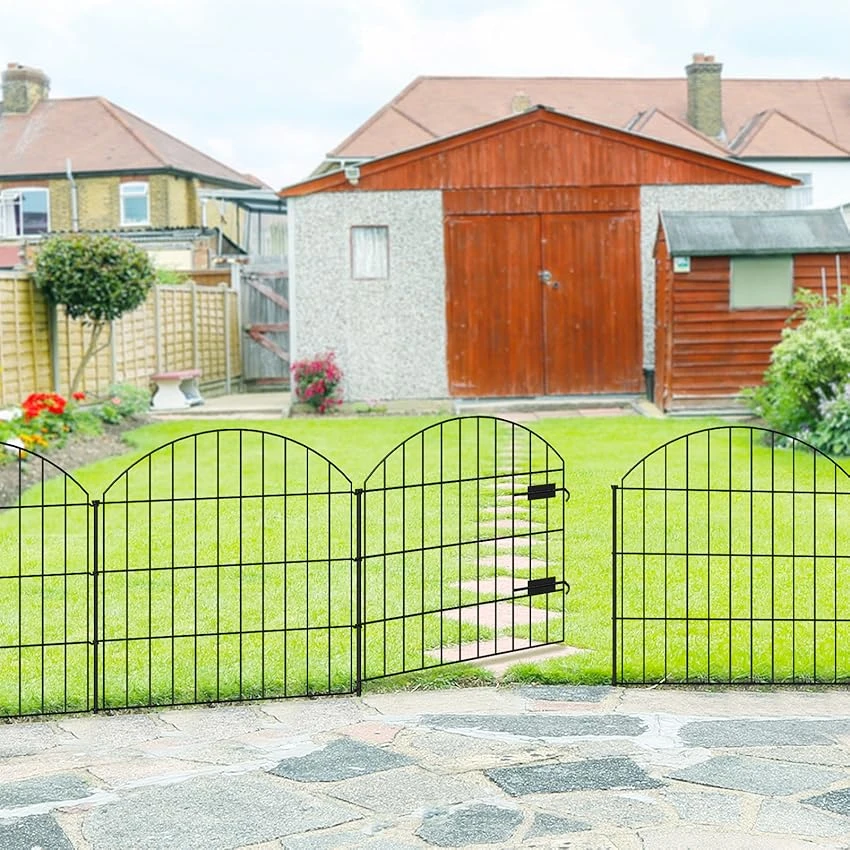
4. Vinyl Fences These fences are low-maintenance and often used for aesthetic purposes. While they may not be as robust as barbed or woven wire fences, they serve well in areas requiring visibility and decorum.
Each type of fence comes with its advantages and disadvantages, and the selection depends on factors such as the type of livestock, the lay of the land, and budget considerations.
Functions of Field Fences
field fences
The primary function of field fences is to delineate boundaries. They mark the limits of private property and prevent animals from wandering into neighboring fields. This not only protects the livestock from potential dangers but also safeguards crops from being destroyed by hungry animals.
Moreover, field fences serve to protect livestock from predators
. Farmers often face threats from wild animals looking for easy prey. A sturdy fence can provide a first line of defense against these predators, ensuring the safety of the farm's animals.Field fences also contribute to controlling land use. By establishing clear boundaries, farmers can designate specific areas for grazing, planting, or resting fields. This is particularly important in rotational grazing systems, where livestock are moved periodically to allow pasture recovery.
The Significance of Field Fences in Today's Agriculture
In an era where sustainable practices and efficient land use are paramount, field fences play an essential role in promoting responsible agricultural practices. They help reduce overgrazing by allowing farmers to manage how and when their livestock access pastures, thus preserving soil quality and promoting ecosystem health.
Moreover, in regions where communal grazing occurs, fences can delineate private and public grazing areas, helping to avoid disputes among landowners and ensuring that resources are shared sustainably.
The significance of field fences also extends beyond agricultural boundaries. They signify the farmer's commitment to their land, showcasing responsibility and care. A well-maintained fence reflects pride in one’s agricultural practice, instilling confidence in consumers about the quality and ethics behind their food sources.
Conclusion
From protecting livestock to managing land use and maintaining aesthetics, field fences are an indispensable tool in agriculture. As farming continues to evolve, the role of field fences will remain crucial in ensuring efficient land management and the sustainable practice of agriculture. Regardless of the type chosen, these fences represent a farmer's dedication to their craft, safeguarding resources, and upholding the delicate balance of nature and agriculture. Whether rustic or modern, field fences are foundational elements that contribute significantly to the landscape of farming and the overall health of agricultural systems.
















