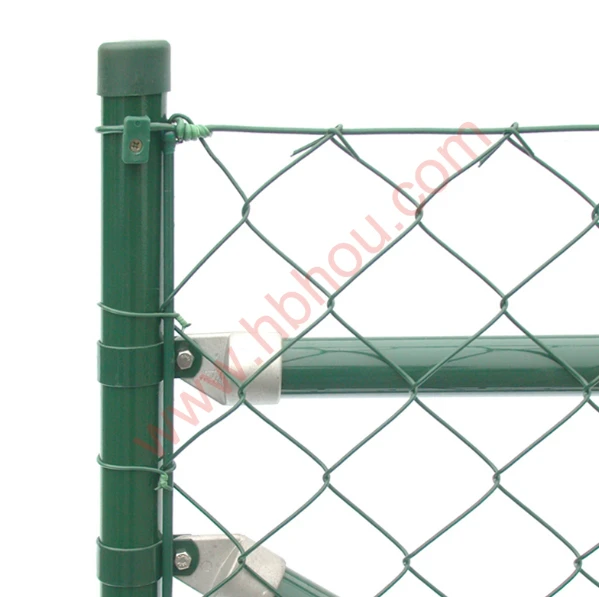
Corral Traps for Capturing Feral Hogs An Effective Management Tool
Feral hogs, also known as feral swine, are an invasive species that have proliferated across the United States and many parts of the world. Their rapid reproduction and adaptability to various environments make them a significant threat to agriculture, ecosystems, and public safety. One of the most effective methods for managing feral hog populations is the use of corral traps. This article explores the design, effectiveness, and best practices associated with corral traps for capturing feral hogs.
Understanding Feral Hogs
Feral hogs are descendants of domestic pigs that have reverted to a wild state. They are highly intelligent and social animals, often traveling in groups called sounders. Each sounder can range from a few individuals to over a dozen, complicating efforts to control their populations. Feral hogs are known for their destructive foraging habits, which can devastate crops, degrade natural habitats, and contribute to erosion. Additionally, they can carry diseases that pose risks to livestock and humans, making their management a priority for farmers and wildlife managers alike.
What are Corral Traps?
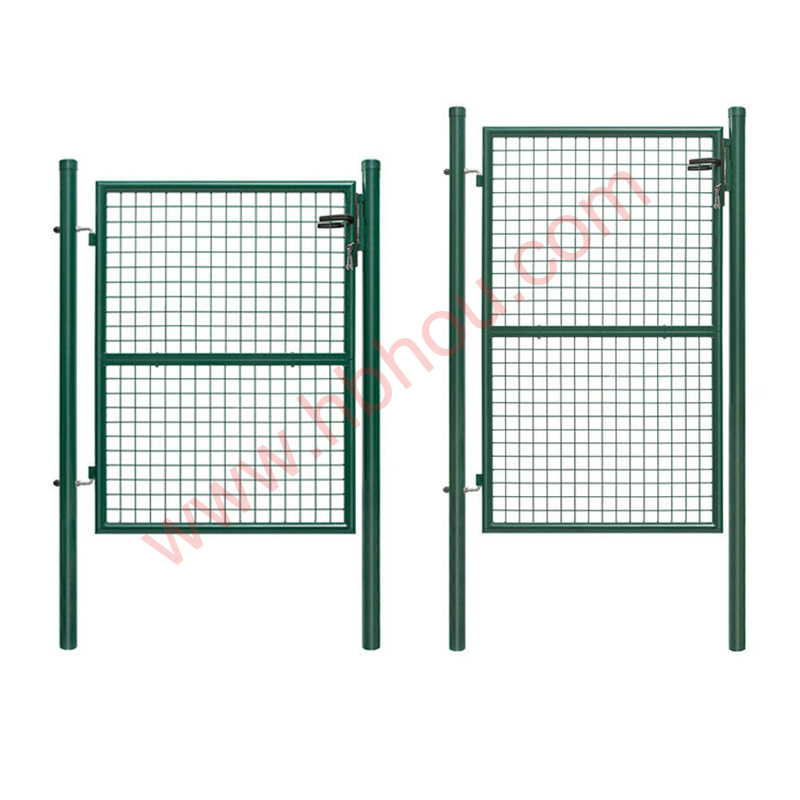
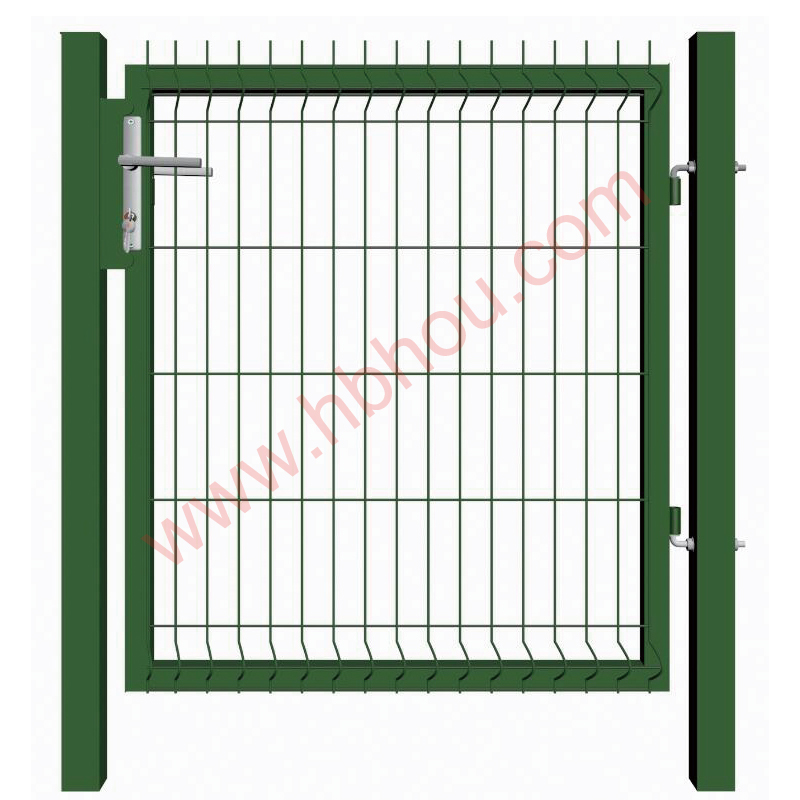
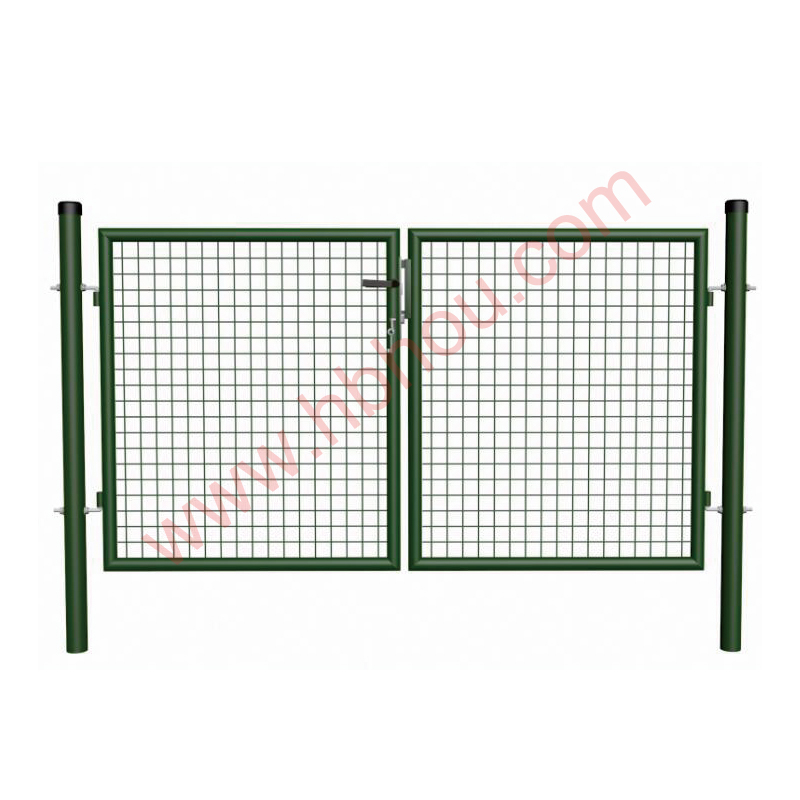
Corral traps are large, fenced enclosures designed to capture multiple hogs at once. These traps typically feature a one-way gate that allows hogs to enter but prevents them from escaping. The design usually includes panels made of heavy-duty materials to withstand the strength and weight of adult hogs. Depending on the design, corral traps can range in size, but most are large enough to accommodate several hogs simultaneously, increasing the efficiency of the capture process.
Advantages of Corral Traps
1. Efficiency Corral traps are ideal for capturing multiple feral hogs in a single operation, reducing the time and resources needed for management efforts. This efficiency is particularly beneficial for landowners dealing with large sounders.
2. Humane Handling When properly designed and monitored, corral traps can minimize stress and injury to captured hogs. This humane aspect is crucial for wildlife managers who must adhere to ethical standards in animal control.
corral traps for capturing feral hogs
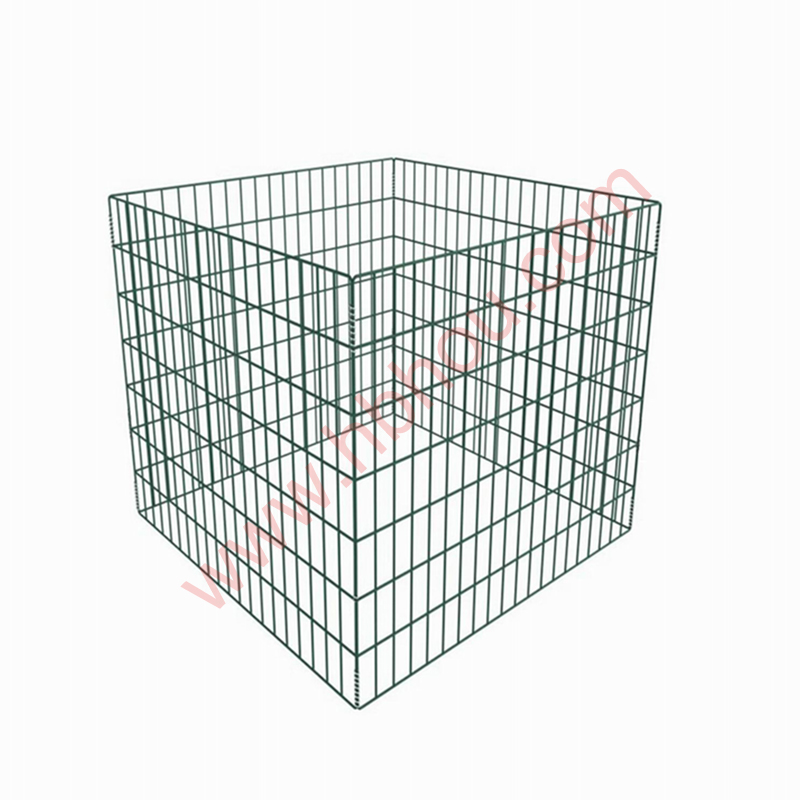
4. Cost-Effective Although there is an initial investment in constructing a sturdy corral trap, the costs associated with capturing and managing feral hogs can be significantly lower than other methods, such as aerial shooting or professional trapping services.
Best Practices for Using Corral Traps
To achieve optimal results with corral traps, several best practices should be followed
1. Site Selection Choose a location with high feral hog activity, such as near feeding areas or water sources. Observing hog behavior can help determine the best placement for the trap.
2. Baiting Effective baiting is critical for attracting hogs into the corral trap. Common baits include corn, bread, and commercial hog attractants. It’s advisable to pre-bait the area (placing bait without the trap initially) to build hog confidence and increase trapping success.
3. Monitoring Regularly check the trap to monitor its activity and ensure captured hogs do not suffer from overheating or injury while waiting for transport. Provides adequate shade and water within the trap doesn’t hurt.
4. Deployment Timing Feral hogs are most active during dawn and dusk. Setting traps during these peak times can increase the likelihood of capturing hogs.
5. Regular Maintenance Ensure that the trap is in good repair to prevent escapes and maintain effectiveness. Check for damage caused by captured hogs or environmental factors.
Conclusion
Corral traps represent a highly effective tool for managing feral hog populations and mitigating their negative impacts on ecosystems and agriculture. By following best practices and understanding the behavior of these animals, landowners and wildlife managers can harness the benefits of this trapping method. With ongoing education and adaptability, corral traps can play a pivotal role in controlling feral hog numbers, safeguarding agricultural interests, and protecting native wildlife. As collaboration among communities, agricultural interests, and wildlife agencies continues, trapping efforts will become even more effective, contributing to the overall goal of managing this challenging invasive species.
















